Click
Here to return to the previous page
Paul Sparks
- Xiangtan University, Online Postgraduate (Masters Degree) English Lesson Plans, Lesson Material and Ideas...
Speaking Lesson: BRITISH CULTURE
LESSON OBJECTIVES:
This lesson will help to make students aware of British culture.
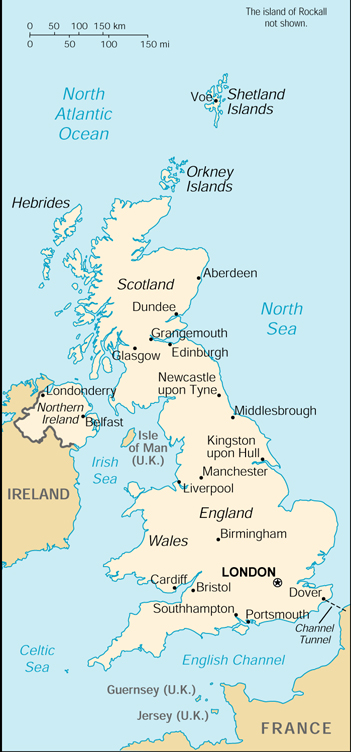 Geography:
The "United Kingdom" consists of England, Wales, Scotland,
Northern Ireland and some small islands around the mainland. "Great
Britain" is only England, Scotland and Wales. Geography:
The "United Kingdom" consists of England, Wales, Scotland,
Northern Ireland and some small islands around the mainland. "Great
Britain" is only England, Scotland and Wales.
Population:
Britain's population has changed rapidly since the 1970’s, when people
from the West Indies, India, Pakistan, Africa, and China began moving into
the UK.
England:
-
Area: 129,720 square
km (50,085 square miles)
-
Population: 51
million
-
Capital city: London
-
Major industries:
Banking and finance, steel, transport equipment, oil and gas, tourism
-
Weather: England's
climate is mild and damp. Temperatures inland don't get much below
freezing in winter (December to February), or much above 30°C (86°F)
in summer (June to August). The north is the coldest area; London, the
south-east and the West Country are the warmest. Rainfall is greatest in
hilly areas and in the West Country. You can expect cloudy weather and
light drizzle in any part of England at any time.
Scotland:
-
Area: 78,772 sq. km
(30,414 sq. mi)
-
Population: 5.1
million
-
Capital city:
Edinburgh
-
Language: English,
Gaelic
-
Major industries:
Banking and finance, steel, transport equipment, oil and gas, whisky,
tourism
-
Weather: There are
wide variations in climate over small distances, and a sunny day will
often as not be followed by a rainy one. The Highlands can have extreme
weather at any time. The east coast tends to be cool and dry, with
winter temperatures rarely dropping below freezing (but watch out for
chilling winds off the North Sea). The west coast is milder and wetter,
with average summer highs of 19°C (66°F). May and June are the driest
months; July and August the warmest.
Wales:
-
Area: 20,764 sq. km
(8017 sq. mi)
-
Population: 2.9
million
-
Capital city:
Cardiff
-
Language: Welsh,
English
-
Major industries:
Agriculture and forestry, manufacturing, tourism
-
Weather: Wales
suffers from an excess of rainfall, with water falling from the sky all
year round. Westerly and south-westerly winds can also make life pretty
miserable. The closeness of the mountains to the coast means that you
can encounter very different climatic conditions within short distances.
Temperatures in Cardiff get up to 20°C (68°F) at the height of summer
(August), but rarely drop below freezing even in the depths of winter
(January).
Northern Ireland:
-
Area: 14,139 sq. km
-
Population: 1.6
million
-
Capital city: Dublin
-
Language: English,
Irish
-
Major industries:
Computer software, information technology, food products, brewing,
textiles, clothing, pharmaceuticals, tourism.
-
Weather: The
temperature only drops below freezing intermittently during the winter
and snow is scarce. Summers aren't very hot, rarely hitting 30° C (86°
F), but they're comfortable and it stays light until around 11pm.
Whatever the time of year, be prepared for rain because Ireland is wet.
The heaviest rain usually falls where the scenery is best, such as
around Kerry, which can be drizzle bound on as many as 270 days of the
year.
Language:
Although English is the universal language of Great Britain there are other
languages such as Welsh which is spoken by about a quarter of Welsh people.
Scotland also has its own language with about 60,000 speakers of the
Scottish language known as Gaelic. The relatively small size of the UK often
leads people to assume that the language spoken is the same, however first
time visitors to the UK are often surprised to find that they have
difficulty in understanding the accents and dialects of certain regions.
Even within the country of England alone there is great diversity of dialect
both regionally and socially. Accents are clues to where people were born
and where they grew up. Although some people may change the way they speak
during their lifetimes, most people carry at least some trace of their
accent and dialect origins throughout their lives. It is common in Britain
for people who display particularly strong accents to be labelled by terms
such as "Geordie", "Cockney", "Jock" or "Scouse."
All of these identify a specific regional accent, most of which are
recognizable to many of the people in the country.
-
Cockney accent =
London
-
Geordie accent =
Newcastle
-
Jock accent =
Scotland
-
Scouse accent =
Liverpool
-
There are many other
names for different accents from different areas.
Accents are often
characterized by British speakers themselves as either "posh" or
"common" accents.
Social Class:
Britain can be divided up into areas, but in the 1940's and 1950's (and
before) it could also be divided up by social class (and to some extent
still can be today). The phrases used are normally "Working
Class", "Middle Class" and "Upper Class". These
classes were to divide people up by the type of work that they did and by
their income. Middle class is also sometimes divided up into "Lower
Middle Class" and "Upper Middle Class". In the early 1900's
about 60% of people were "Working Class" and over 30% "Middle
Class", with less than 10% in the Upper Class category, also referred
to as the "Aristocracy". A typical middle class person may be a
doctor or a teacher, whilst working class are factory workers. Manual
workers are also known as "Blue collar" workers, whilst office
staff are known as "White Collar" workers. Class can also be
decided upon which newspaper a person reads or what type of television
programmes that they watch. Class can also be determined by what type of
education a person has.
Race:
The UK is made up of people from many different races. It is not now a
"white" country. A majority of immigrants arrived in the UK in the
last 40 years. People from countries who used to be part of the British
Empire were allowed to move to the UK to live. Immigrants bring many
cultures into the UK, and also many other foods. The most common foods in
the UK are now Indian Curry and Chinese food. British music has benefited
form immigrants, with many black artists becoming very popular. Many
immigrants bring different religions into the UK - there is now a large
Muslim community in the UK. However, the mix of races can cause some
problems, some white people do not like the growing number of ethnic
minorities in the UK. Some cities have higher populations of ethnic
minorities than others, London has over 30% of the population from non white
groups. It is now illegal to discriminate between black and white people, or
anyone from another race in the UK.
British Politics:
In British politics there are elections about every 4 years, The elections
are to decide which of the political parties ("political parties"
= "political groups") will be allowed to form a government and run
the country. The three main political parties are: "Labour",
"Conservative" and "Liberal Democrat". The UK has a
"Prime Minister", but no President. The building where politics
takes place is called "The Houses of Parliament". This is a place
which is made up of 2 "houses": "The House of Commons"
and "The House of Lords". The House of Commons is where the
government debate issues with the other political parties. It is made up of
Members of Parliament (MP's) from all political parties who are voted for in
local elections around the UK. The House of Lords is traditionally made up
of "Lords" who received the title from their father or were given
the title for achievements. The House of Lords is now changing so that it is
made up of many other people, not just people who inherited the title from
their father. When the House of Commons wants to make or change a law they
will give a draft version to the House of Lords, who then debate the issue
further, and if they agree with the proposal from the House of Commons then
the law will be passed.
 The
Royal Family (Monarchy): On 29th July 1981
Prince Charles, The Prince of Wales, married Lady Diana Spencer. They
divorced on 28th August 1996. The Princess of Wales was killed one year
later in a car crash on 31st August 1997 in Paris. Their two children,
Prince William and Prince Henry, are second and third in line of succession
to the throne. The current Queen is Elizabeth the second. She is not only
Queen of the United Kingdom, but also the head of the Commonwealth, a
voluntary association of 54 independent countries. Most of these countries
were part of the British Empire, but are now independent. The Commonwealth
is now used for international co-operation and trade links. The Royal Family
do not have any political power now, although the Queen does meet regularly
with the Prime minister and is required to agree to any new laws. The
Royal Family (Monarchy): On 29th July 1981
Prince Charles, The Prince of Wales, married Lady Diana Spencer. They
divorced on 28th August 1996. The Princess of Wales was killed one year
later in a car crash on 31st August 1997 in Paris. Their two children,
Prince William and Prince Henry, are second and third in line of succession
to the throne. The current Queen is Elizabeth the second. She is not only
Queen of the United Kingdom, but also the head of the Commonwealth, a
voluntary association of 54 independent countries. Most of these countries
were part of the British Empire, but are now independent. The Commonwealth
is now used for international co-operation and trade links. The Royal Family
do not have any political power now, although the Queen does meet regularly
with the Prime minister and is required to agree to any new laws.
Housing:
There are many different styles of houses in the UK. In the countryside
there are many old buildings, farms and cottages, normally built from stone
and many are hundreds of years old. There are also modern buildings in the
countryside but there are many building restrictions to stop people building
in certain areas of the countryside. Most people live in, or around a city
or town in the UK. The price of houses is normally more expensive in city
centres. House prices vary between different areas of the UK, the South of
England is very expensive compared to the North. The main style of British
houses are as follows:
-
Terraced house -
Long rows of houses joined together, built for working class people,
such as coal miners.
-
Bungalow - A house
which is only on one level, with no stairs. Suitable for older people or
small families.
-
Detached - A house
which is not joined to any other, detached houses are normally more
expensive.
-
Semi-Detached - This
is when 2 houses are joined together, usually with their own gardens.
-
Flat (apartment) -
In some areas where house prices are more expensive people might live in
a flat.
Food & Drink:
Although everyone in Britain understands that "breakfast" is the
first meal of the day. There is a lot of confusion about the words for other
meals such as "dinner", "tea", "elevensees",
"brunch", "supper" etc. and if you ask a British person
what these words mean, most of them will give you a different answer.
Mealtimes are as follows:
-
Breakfast (usually
sometime between 7am - 9am)
-
Mid-Morning Snack
(10am or 11am)
-
Lunch (12:00 midday
to 1pm or 1pm - 2pm)
-
Afternoon Break
(About 3pm)
-
Dinner (usually
sometime between 6pm to 9pm)
-
Supper (before bed)
Breakfast - Many British
people do not have breakfast, they prefer to have a cup of tea or coffee or
a glass of milk, then have a morning snack when they are at work. A
traditional English breakfast is a fried meal of eggs, bacon and sausages.
However, most people now have either breakfast cereal or toast with jam or
marmalade. In Scotland many people eat porridge or boiled oats.
Mid Morning Snack -
Workers in the UK are entitled to a morning break under the British
employment laws. The break is normally around 20 minutes. Most people will
have a cup of tea or coffee, or a soft drink with biscuits, cake or
chocolate bars etc. However most employers will allow workers to have
unlimited coffee or tea breaks throughout the day whilst they work. The
common name given to a morning break is "10 o'clock" or
"Elevensees".
Lunch - Workers in the
UK are entitled to a one hour lunch break. This is typically either 12:00
midday until 1pm, or 1pm until 2pm. Lunch is normally a small meal, such as
sandwiches, but it might be a full meal. Elderly people tend to have their
biggest meal at lunchtime and a lighter meal in the evening, so they might
refer to the midday meal as "dinner"!. Many children and some
workers are given a "packed lunch" to eat, some factories and
schools have canteens where you can buy food. A packed lunch normally
consist of some sandwiches, a packet of crisps, an apple and a can of
something to drink, for example, Coca-Cola.
Afternoon Break - At
about 3pm workers will have another break, a cup of tea or coffee, or soft
drinks and snack food.
 Dinner
- The meal in the evening is normally called Dinner, but may also be
referred to as "Tea". The evening meal can be any time after 4pm,
but is usually between 6pm and 9pm. Some families may eat this meal
together, however many families now eat the meal in front of the television
rather than sitting at a table. British food is changing and most British
people eat meals from many different countries, for example spaghetti from
Italy or curry from India. The most typical meal for dinner is "meat
and two vegetables". This consists of a piece of meat accompanied by
two different boiled vegetables. This is covered with "gravy"
which is a sauce made with the juice that was obtained when the meat was
cooked. One of the vegetables is almost always potatoes, the British eat a
lot of potatoes. At the end of dinner there is normally a pudding or
dessert, such as apple pie, ice cream or trifle. Dinner
- The meal in the evening is normally called Dinner, but may also be
referred to as "Tea". The evening meal can be any time after 4pm,
but is usually between 6pm and 9pm. Some families may eat this meal
together, however many families now eat the meal in front of the television
rather than sitting at a table. British food is changing and most British
people eat meals from many different countries, for example spaghetti from
Italy or curry from India. The most typical meal for dinner is "meat
and two vegetables". This consists of a piece of meat accompanied by
two different boiled vegetables. This is covered with "gravy"
which is a sauce made with the juice that was obtained when the meat was
cooked. One of the vegetables is almost always potatoes, the British eat a
lot of potatoes. At the end of dinner there is normally a pudding or
dessert, such as apple pie, ice cream or trifle.
Supper - A light snack
before bed, after dinner. Normally now only for elderly people, it was
traditional in Britain a number of years ago to eat supper.
Snacks - British people
eat a lot of food in between meals, they will have many snacks, including
chocolate, crisps, soft drinks, tea, coffee, cakes, biscuits etc. at any
time of the day or night.
On Sundays many people
don't have to work so they take the opportunity eat together with their
family. Sunday lunch is usually the best meal of the week and many of the
meals which are considered typically British are eaten for Sunday lunch. For
example roast beef and Yorkshire pudding. Yorkshire pudding is a batter made
with flour, eggs and milk and cooked in the oven. This is most often eaten
with roast beef for Sunday lunch.
 Fast
Food - KFC, McDonald's and other fast food style restaurants are very
popular in the UK. Many bars now serve food, good quality, traditional meals
which are cheaper than restaurants, but healthier than fast food. Fast
Food - KFC, McDonald's and other fast food style restaurants are very
popular in the UK. Many bars now serve food, good quality, traditional meals
which are cheaper than restaurants, but healthier than fast food.
Fish shop sell
"fish 'n' chips", fried potatoes called chips with fish and a
choice of pies, mushy peas, etc. The chips are wrapped in newspaper and
eaten outside or taken home. It is traditional to eat fish and chips on a
Friday night, but fish and chips are common throughout the week.
Pizza is traditionally
from Italy, however the food has now become very popular in the UK. You can
eat pizza in a restaurant or take it home to eat, you can also have pizza
delivered to your home if you have a local delivery shop.
Curry is now the most
popular food in the UK. It is originally from India, there are many Indian
restaurants in the UK, some where you can stay and eat, and others which
serve takeaway food. It is normally served with rice. Curry can be a very
hot and spicy food, but there are different types of curry. As well as
Indian food, the UK has many Chinese restaurants and takeaways. Chinese food
is very popular with British people. However not many British people can use
chopsticks, they prefer to eat from a plate with a knife and fork.
Fashion:
British fashion changes quickly, styles, colours etc. are often changing. In
the 1950's high heel shoes became very fashionable for women. 1960's
fashions were from what people saw on television and influenced by Rock 'n'
Roll music. The late 60's used flowers and hippie fashion, mini skirts and
long hair started a fashion trend that would last two decades. The 1970s
were the "anything goes" decade. For some, the uglier and chunkier
the fashion, the better. For others, soft and feminine was the answer.
Polyester knitted fabrics broke the ground to expand the continuing look. If
you didn't wear polyester, the preferred textile was denim blue jeans.
Television and film reflected the way people dressed. The 1980's was all
about money, money to be made, money to be spent, and you had to look
really, really good while you were spending it. The 90's saw a return of
different fashions from previous decades.
|